Small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMOs) are tiny but important protein regulators involved in orchestrating a broad spectrum of biological processes,
more details >>>
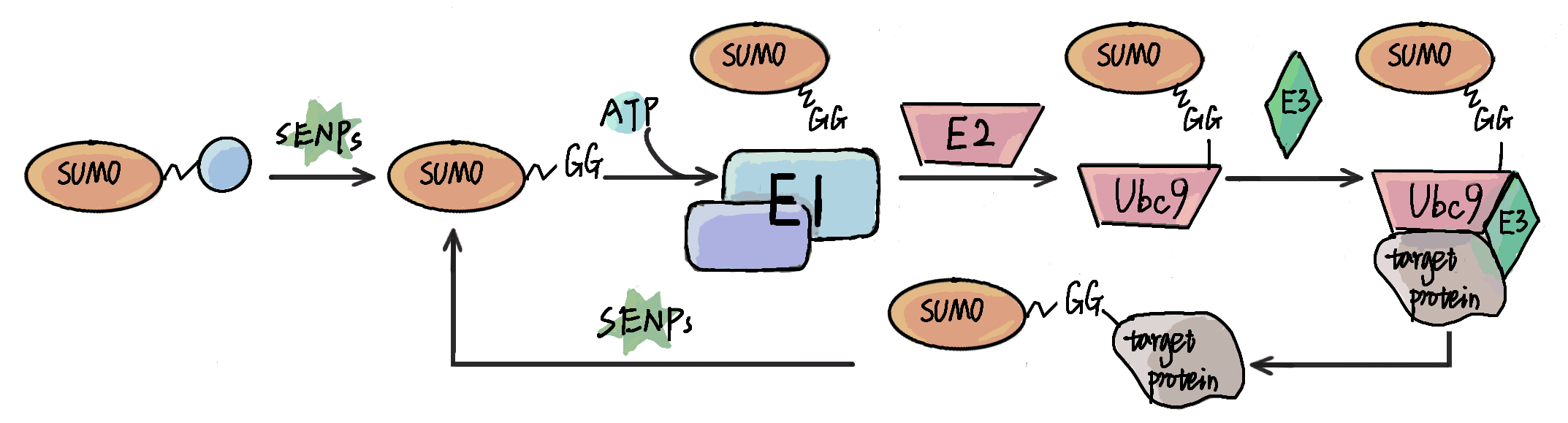
either by covalently modifying protein substrates, or by non-covalently interacting with other proteins. The identification of SUMOylation sites and SUMO-interacting motifs (SIMs) in proteins is fundamental for better understanding SUMOs.
Here, we developed an updated online service, GPS-SUMO 2.0, using a non-redundant and non-homologous data set of 59,069
SUMOylation sites in 10,762
proteins and 163 SIMs in 102 proteins. For prediction of SUMOylation sites and SIMs, we integrated 11 types of sequence
features and 3 machine learning algorithms, including penalized logistic regression (PLR), deep neural network (DNN), and Transformer. For users, one or multiple protein sequences or identifiers could be inputted, while the prediction results will be shown in a tabular list. Besides the basic statistics, we integrated the knowledge of 35 public resources to annotate SUMOylation sites or SIMs, including but not limited to the experimental evidence, physical interactions, 3D structures, and disorder propensities. We believe that GPS-SUMO 2.0 can serve as a useful service for further analysis of SUMOs.
Hide details <<<
Below, we provide the basic predictor based on penalized logistic regression + GSEA. Speed:
Speed:




For the help of GPS-SUMO 2.0 and the tutorial, please refer to the USER GUIDE page.
For the sourse code of GPS-SUMO 2.0, please visit the GitHub page.
For the advanced predictors, please visit the ADVANCED page.

![]() Speed:
Speed:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()






 GPS-SUMO 2.0: an updated online service for the prediction of SUMOylation sites and SUMO-interacting motifs.
GPS-SUMO 2.0: an updated online service for the prediction of SUMOylation sites and SUMO-interacting motifs. Systematic study
of protein sumoylation: Development of a site-specific predictor
of SUMOsp 2.0.
Systematic study
of protein sumoylation: Development of a site-specific predictor
of SUMOsp 2.0.